What is a Sensor ?
There are numerous definitions as to what a sensor is but I would like to define a Sensor as an input device which provides an output (signal) with respect to a specific physical quantity (input).
The term “input device” in the definition of a Sensor means that it is part of a bigger system which provides input to a main control system (like a Processor or a Microcontroller).
Another unique definition of a Sensor is as follows: It is a device that converts signals from one energy domain to electrical domain. The definition of the Sensor can be understood if we take an example in to consideration.
The simplest example of a sensor is an LDR or a Light Dependent Resistor. It is a device, whose resistance varies according to intensity of light it is subjected to. When the light falling on an LDR is more, its resistance becomes very less and when the light is less, well, the resistance of the LDR becomes very high.
We can connect this LDR in a voltage divider (along with other resistor) and check the voltage drop across the LDR. This voltage can be calibrated to the amount of light falling on the LDR. Hence, a Light Sensor.
Now that we have seen what a sensor is, we will proceed further with the classification of Sensors.
Different Types of Sensors :-
We live in a World of Sensors. You can find different types of Sensors in our homes, offices, cars etc. working to make our lives easier by turning on the lights by detecting our presence, adjusting the room temperature, detect smoke or fire, make us delicious coffee, open garage doors as soon as our car is near the door and many other tasks.
All these and many other automation tasks are possible because of Sensors. Before going in to the details of What is a Sensor, What are the Different Types of Sensors and Applications of these different types of Sensors, we will first take a look at a simple example of an automated system, which is possible because of Sensors (and many other components as well).
Classification of Sensors :-
There are several classifications of sensors made by different authors and experts. Some are very simple and some are very complex. The following classification of sensors may already be used by an expert in the subject but this is a very simple classification of sensors.
In the first classification of the sensors, they are divided in to Active and Passive. Active Sensors are those which require an external excitation signal or a power signal.
Passive Sensors, on the other hand, do not require any external power signal and directly generates output response.
The other type of classification is based on the means of detection used in the sensor. Some of the means of detection are Electric, Biological, Chemical, Radioactive etc.
The next classification is based on conversion phenomenon i.e. the input and the output. Some of the common conversion phenomena are Photoelectric, Thermoelectric, Electrochemical, Electromagnetic, Thermooptic, etc.
The final classification of the sensors are Analog and Digital Sensors. Analog Sensors produce an analog output i.e. a continuous output signal with respect to the quantity being measured.
Digital Sensors, in contrast to Analog Sensors, work with discrete or digital data. The data in digital sensors, which is used for conversion and transmission, is digital in nature.
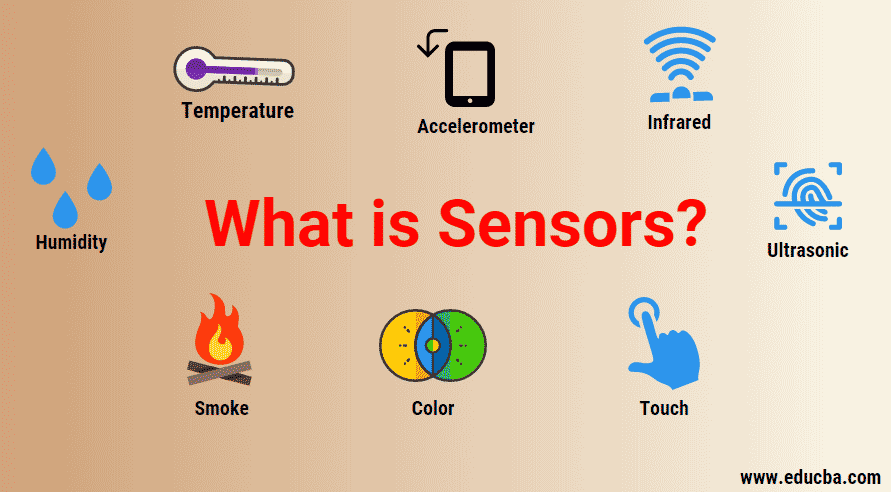
The following is a list of different types of sensors that are commonly used in various applications. All these sensors are used for measuring one of the physical properties like Temperature, Resistance, Capacitance, Conduction, Heat Transfer etc.
- Temperature Sensor
- Proximity Sensor
- Accelerometer
- IR Sensor (Infrared Sensor)
- Pressure Sensor
- Light Sensor
- Ultrasonic Sensor
- Smoke, Gas and Alcohol Sensor
- Touch Sensor
- Color Sensor
- Humidity Sensor
- Tilt Sensor
- Flow and Level Sensor
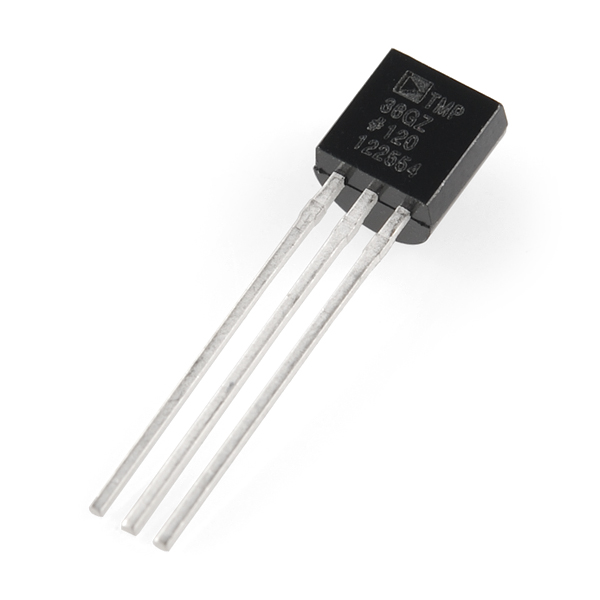
Temperature Sensor :-
One of the most common and most popular sensor is the Temperature Sensor. A Temperature Sensor, as the name suggests, senses the temperature i.e. it measures the changes in the temperature.
In a Temperature Sensor, the changes in the Temperature correspond to change in its physical property like resistance or voltage.
There are different types of Temperature Sensors like Temperature Sensor ICs (like LM35), Thermistors, Thermocouples, RTD (Resistive Temperature Devices), etc.
Temperature Sensors are used everywhere like computers, mobile phones, automobiles, air conditioning systems, industries etc.
A simple project using LM35 (Celsius Scale Temperature Sensor) is implemented in this project: TEMPERATURE CONTROLLED SYSTEM.
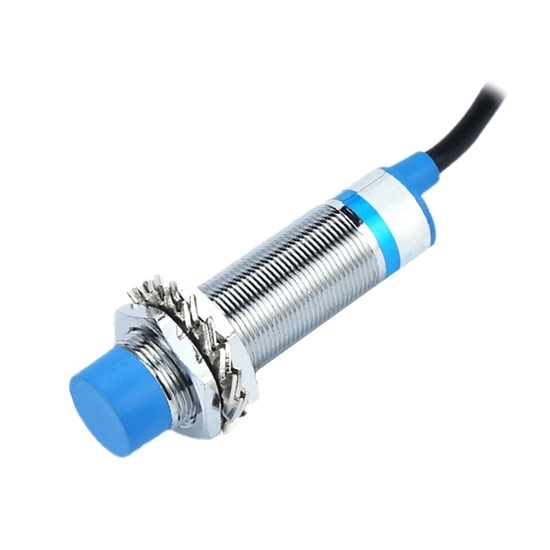
Proximity Sensors :-
A Proximity Sensor is a non-contact type sensor that detects the presence of an object. Proximity Sensors can be implemented using different techniques like Optical (like Infrared or Laser), Ultrasonic, Hall Effect, Capacitive, etc.
Some of the applications of Proximity Sensors are Mobile Phones, Cars (Parking Sensors), industries (object alignment), Ground Proximity in Aircrafts, etc.
Proximity Sensor in Reverse Parking is implemented in this Project: REVERSE PARKING SENSOR CIRCUIT
Infrared Sensor (IR Sensor) :-
IR Sensors or Infrared Sensor are light based sensor that are used in various applications like Proximity and Object Detection. IR Sensors are used as proximity sensors in almost all mobile phones.
There are two types of Infrared or IR Sensors: Transmissive Type and Reflective Type. In Transmissive Type IR Sensor, the IR Transmitter (usually an IR LED) and the IR Detector (usually a Photo Diode) are positioned facing each other so that when an object passes between them, the sensor detects the object.
The other type of IR Sensor is a Reflective Type IR Sensor. In this, the transmitter and the detector are positioned adjacent to each other facing the object. When an object comes in front of the sensor, the sensor detects the object.
Different applications where IR Sensor is implemented are Mobile Phones, Robots, Industrial assembly, automobiles etc.
A small project, where IR Sensors are used to turn on street lights: STREET LIGHTS USING IR SENSORS.
Ultrasonic Sensor :-
An Ultrasonic Sensor is a non-contact type device that can be used to measure distance as well as velocity of an object. An Ultrasonic Sensor works based on the properties of the sound waves with frequency greater than that of the human audible range.
Using the time of flight of the sound wave, an Ultrasonic Sensor can measure the distance of the object (similar to SONAR). The Doppler Shift property of the sound wave is used to measure the velocity of an object.
Arduino based Range Finder is a simple project using Ultrasonic Sensor: PORTABLE ULTRASONIC RANGE METER.
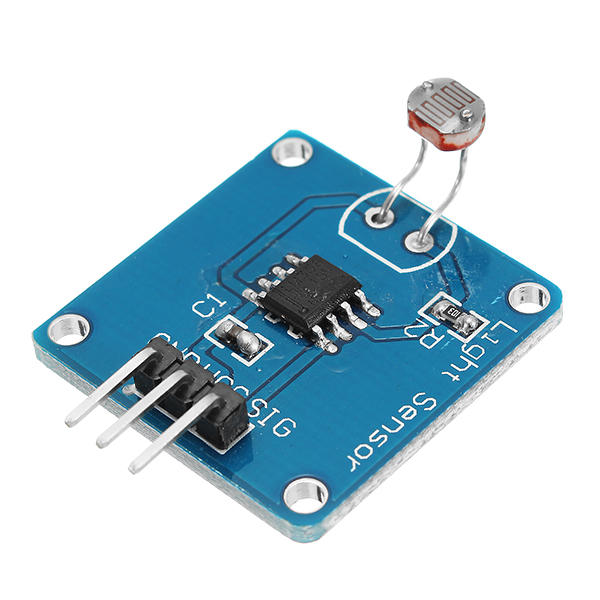
Light Sensor :-
The light sensor is a passive devices that convert this “light energy” whether visible or in the infra-red parts of the spectrum into an electrical signal output. Light sensors are more commonly known as “Photoelectric Devices” or “Photo Sensors” because the convert light energy (photons) into electricity (electrons).
Smoke Sensor :-
Photoelectric alarms (Smoke Sensor) work using a photoelectric sensor and a light source. As smoke enters the chamber and crosses the path of the light beam, light is scattered by the smoke particles, aiming it toward the sensor, which in turn triggers the alarm.
Alcohol Sensor :-
An alcohol sensor detects the attentiveness of alcohol gas in the air and an analog voltage is an output reading. The sensor can activate at temperatures ranging from -10 to 50° C with a power supply is less than 150 Ma to 5V. The sensing range is from 0.04 mg/L to 4 mg/L, which is suitable for breathalyzers.
Touch Sensor :-
Touch sensor is similar to that of a simple switch. When there is contact with the surface of the touch sensor, the circuit is closed inside the sensor and there is a flow of current. ... The measurement circuit will detect the change in the capacitance and converts it into a trigger signal.
Colour Sensor :-
The light sensor works by shining a white light at an object and then recording the reflected colour. It can also record the intensity of the reflection (brightness). Through red, green and blue colour filters the photodiode converts the amount of light to current.
Humidity Sensor :-
A humidity sensor (or hygrometer) senses, measures and reports both moisture and air temperature. ... Relative humidity becomes an important factor when looking for comfort. A sample humidity sensor. Humidity sensors work by detecting changes that alter electrical currents or temperature in the air.
Tilt Sensor :-
.












No comments:
Post a Comment